Low testosterone levels can be a concern in terms of sexual health, but also physical health. Signs of aging, such as fatigue, low energy, and often have the same underlying cause: low testosterone levels. This calls for Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT).
Declining natural testosterone levels are the reason why the diet and lifestyle that worked for a person in their 20s or 30s will fail as they grow older. This shift has a significant impact on body composition, energy levels, libido, and sleep. To help restore the natural hormone balance, many are prescribed Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT).
Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT) is a widely discussed topic, but many people are unaware of its basics. Let’s take a look at what Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT) is from a beginner’s point of view.
An In-depth Look at TRT
Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT) is a form of low testosterone treatment that helps restore testosterone to normal levels. Among men, it is the most effective treatment route for men who are suffering from hypogonadism and associated conditions. In women, especially post-menopause, TRT can be used to treat low testosterone levels.
Testosterone, the primary androgen, is responsible for regulating mood and cognitive function, bone density, metabolism, muscle mass, and most importantly, sexual health.
How Testosterone Works in The Body
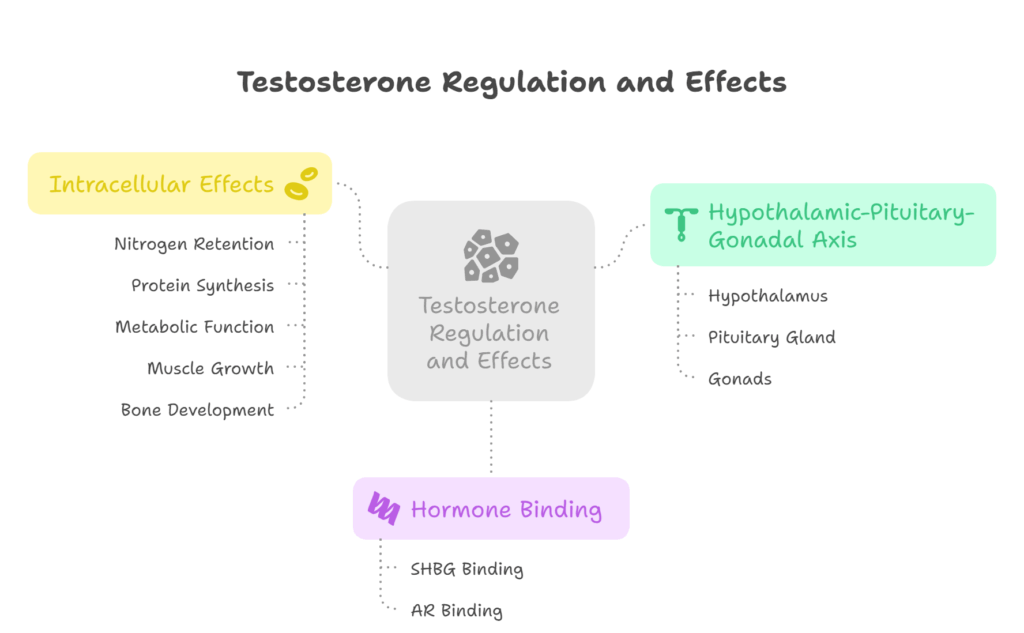
In the human body, testosterone levels and secretion are controlled by the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal (HPG) axis. In the HPG axis, the GnRH from the hypothalamus prompts the pituitary gland to release LH and FSH.
These, in turn, stimulate the Leydig cells (male) and Theca cells (female) to synthesize testosterone. While 98-99% of this binds to sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG) (albumin), the other 1-2% binds to the intracellular androgen receptors (ARs). Here, it stimulates nitrogen retention, protein synthesis, metabolic function, muscle growth, and bone development.
Why Low Testosterone Levels Can Occur
In both men and women, low testosterone levels may occur due to natural aging. Due to the following reasons, one may seek low testosterone treatment with TRT:
- Aging
- Side effects of chemo
- Testicular injury
- Testicular cancer
- Unchecked significant weight gain
- Problems with the pituitary gland
How to Diagnose for Testosterone Replacement Therapy
To learn if a person actually requires testosterone replacement therapy, they may have to undergo the following tests:
- Total Testosterone Test: A blood test that measures the levels of free testosterone and what is bound to proteins.
- Free Testosterone Test: Only measures the level of free testosterone that is not bound to SHBG, to identify particular medical conditions such as infertility, low libido, and muscle weakness.
- Bioavailable Testosterone Test: To identify medical conditions, this test for free testosterone as well as that bound to SHBG (or albumin).
The normal testosterone levels in men may range from 300 to 1000 ng/dL. Among women, it is significantly lower at 15 to 70 ng/dL. TRT may be prescribed if testosterone levels drop beyond this minimum threshold.
During TRT, synthetic forms of testosterone are administered in the form of dermal patches, gels, pellets, oral tablets, or testosterone injections. These replenish the testosterone deficit, restoring natural hormone balance.
Signs and Symptoms of Low Testosterone
Some general signs of low testosterone are:
- Fatigue and low energy
- Loss of muscle mass
- Hair thinning
- Low libido
- Hot flashes
- Difficulty concentrating
- Sleep disturbances
- Mood changes
- Irritability
- Depression
- Decreased bone density
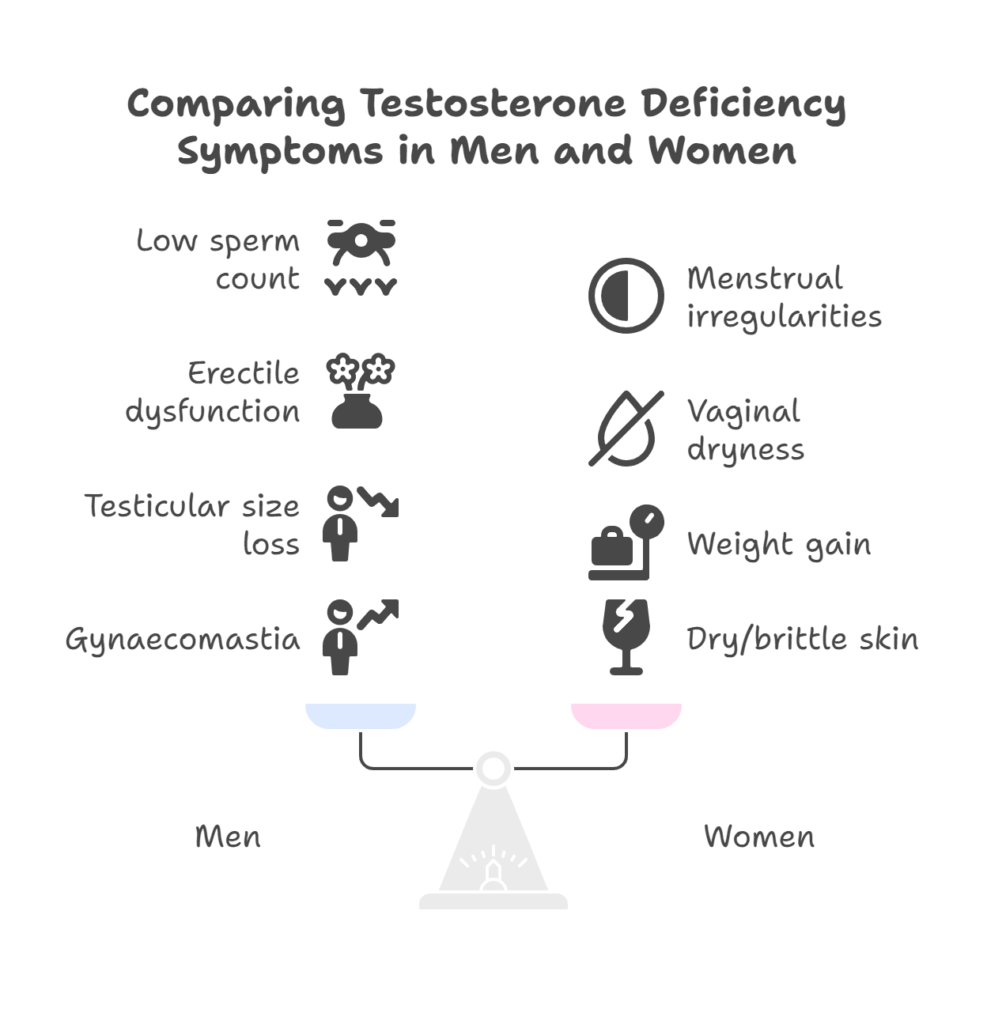
Further, the symptoms of low testosterone in men that necessitate TRT include:
- Low or zero sperm count
- Erectile dysfunction
- Loss of testicular size
- Gynaecomastia (Breast tissue enlargement)
Among women, low testosterone levels may lead to:
- Menstrual irregularities
- Vaginal dryness
- Weight gain
- Dry/ brittle skin
- Loss of bone density
Methods of TRT Administration
For low testosterone treatment, the most common testosterone administration routes and procedures include:
- Injections
Administered both intramuscularly and subcutaneously, testosterone injections are available as synthetic testosterone esters. These are administered at regular intervals, as prescribed, by qualified medical personnel. Though highly effective, testosterone injections involve weekly injections, which can potentially cause peaks and lean periods in hormone levels.
- Topical Gels/Creams
These require daily application on clean, dry skin, as directed by your physician. However, they also pose the risk of skin transfer to others.
- Patches
Testosterone patches offer consistent, discreet dosing and have to be applied daily to the skin. However, those taking patches are asked to change locations to avoid skin irritation.
- Pellets (Implanted Under Skin)
Testosterone pellets are implanted under the skin and can last for 3-6 months. However, if opting for pellets, the person in question will have to undergo a minor procedure for implantation.
- Oral and Buccal Tablets
Buccal testosterone tablets are sticky pills that you apply to your gum, while oral pills are taken with water. While the dosage can be easier to control, testosterone tablets are metabolised in the liver, which may lead to liver stress.
Comparison of Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT) Methods
The following table sheds light on how the different treatment methods for TRT compare:
| Method | How It Works | Pros | Cons | Best For |
| Injections | Injected weekly or bi-weekly | Effective and widely available | Hormone level fluctuations, injection discomfort | Those who want strong results |
| Topical Gels / Creams | Daily application on the skin | Easy to use, steady absorption | Risk of transfer to others, skin irritation, and must be applied daily | Those preferring a non-invasive daily routine |
| Patches | Applied daily to the skin | Convenient, consistent hormone levels | Skin rashes/irritation, less discreet | People seeking stable dosing and easy use |
| Pellets (Implants) | Small pellets inserted under the skin release testosterone for 3–6 months | Long-lasting, no daily routine needed | Minor surgical procedure, infection risk, hard to adjust dose | Those preferring a “set it and forget it” therapy |
| Oral / Buccal Tablets | Pills taken orally or absorbed through the gums | Easy, familiar format | Potential liver side effects | People are unwilling to use injections or topical forms |
Table: Comparison Between the Different TRT Options
Benefits of Testosterone Replacement Therapy
By opting for TRT, people can enjoy the following benefits:
- Improved energy and mood
- Enhanced libido
- Improved sexual health
- Increased muscle mass and strength
- Better bone density and reduced fracture risk
- Potentially improved cognitive health
Risks and Side Effects to Consider
However, TRT, in both men and women, is associated with certain side effects:
- Acne and oily skin
- Hair loss
- Sleep apnea aggravation
- Headaches, nausea, and vomiting
- Blood clots
- Cardiovascular risks
- Liver stress
- Skin irritation
- Fertility reduction
- Mood swings
In men, it may also cause
- Testicular shrinkage
- Gynecomastia
- Decrease in sperm count
- Infertility
- Elevated prostate-specific antigen (PSA)
Additionally, women may face:
- Deepening of the voice
- Changes in body odour
- Menstrual changes
- Clitoral enlargement
- Breast atrophy
Thus, people need to undergo TRT under strict medical supervision and monitoring. Further, it is also important to follow the prescription and not deviate from the prescribed dosage and schedule.
Who Should (and Shouldn’t) Consider TRT?
People who have been diagnosed with low testosterone and need treatment via both blood tests and clinical symptoms can undergo TRT if their doctors prescribe the same.
However, testosterone replacement therapy is not advisable for people with:
- Heart disease, especially a history of heart attack or stroke
- Obstructive sleep apnea
- A history of elevated red blood cell counts
- Untreated prostate cancer
- Male breast cancer
Further, a prescription for TRT will be issued by a doctor only after a thorough medical evaluation.
Lifestyle and Alternatives to Consider Before TRT
Since TRT involves taking synthetic testosterone, which may lead to side effects, it is best to explore natural testosterone supplements and methods before starting TRT.
At times, simple lifestyle changes alone improve testosterone levels. This includes routine weight loss and exercise regimens, improved sleep, better stress management, and balanced nutrition.
Alternatively, natural testosterone supplements such as zinc, ginger, and ashwagandha can improve testosterone levels. Some people also opt for over-the-counter herbal supplements to improve testosterone.
Wrapping Up
Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT) is a tried and tested medical therapy to restore testosterone in men with low levels. While it provides several benefits, it also comes along with several risks. Thus, it is important to avail medical guidance, with testing and proper diagnosis, for TRT.
Get Started With Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT)
Are you experiencing one or more of the symptoms of low testosterone? Consult your doctor and get started on TRT today.
Frequently Asked Questions
To increase testosterone naturally, people can opt for regular exercise, a better diet, proper sleep, and certain natural testosterone supplements such as zinc and vitamin D. For significantly low testosterone levels, people can undergo TRT with testosterone injections, tablets, or others.
The starting dose for TRT among bodybuilders is 100 – 200 mg/week. However, people can be prescribed higher (or lower) doses based on their requirements.
First, you need to undergo the blood tests that show you have low testosterone levels and require TRT. Then you have to get a prescription from your doctor since Testosterone is a Class C medication that cannot be purchased otherwise.
Both Testosterone Enanthate and Cypionate have a similar half-life and efficacy. However, Testosterone Cypionate is available as a subcutaneous injection that offers painless administration.